Dragonfly can be split into 3 components:
- a camera (USB, built-in, network connected) that sends the video stream to the computing unit that runs the Dragonfly Application.
- a computing unit (on which it runs the Dragonfly Application) that receives the video stream from the camera and computes the camera’s position.
- a web interface (Dragonfly Web User Interface) that is accessed with a browser and that is used to configure and monitor the Dragonfly Application.
The 3 components are completely separated. This makes Dragonfly highly versatile and lets you choose between different architectures all described in the next sections.
On board local computation
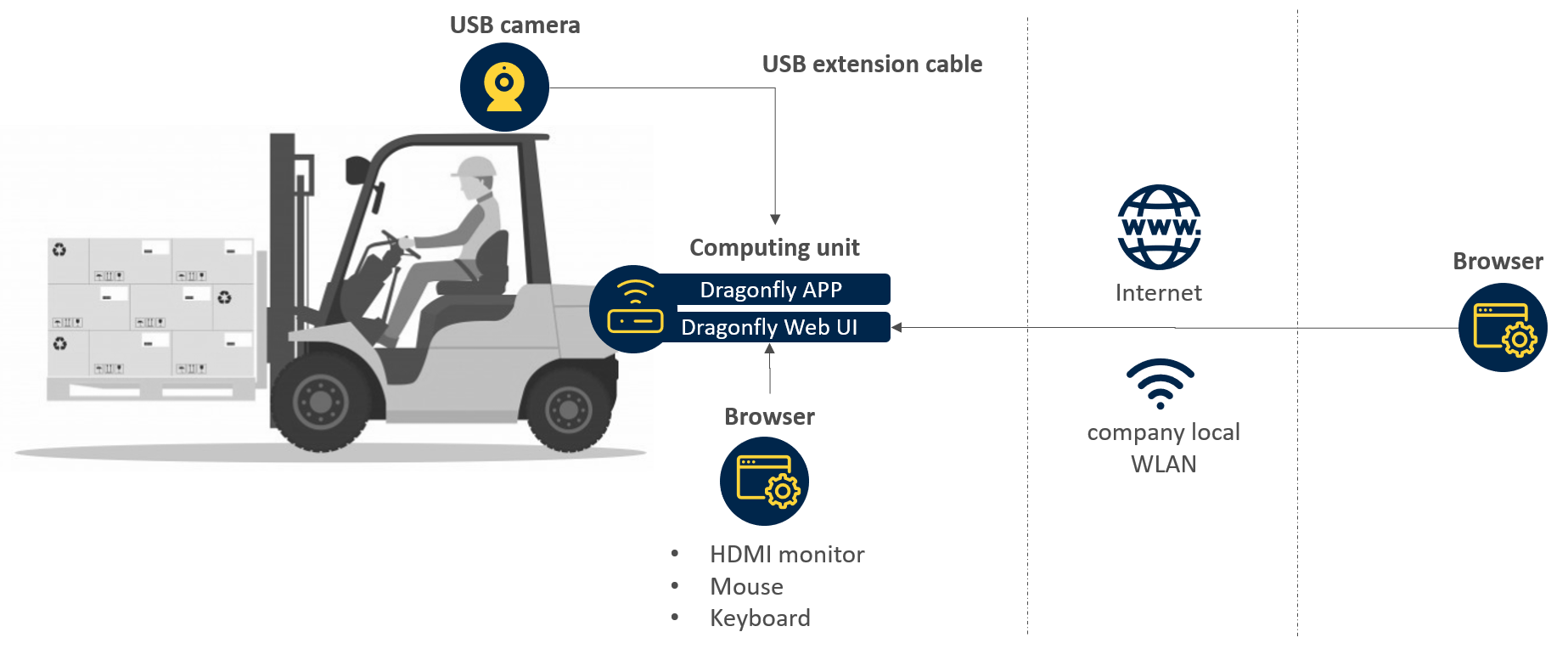 Built-in/USB camera directly connected to the computing unit that runs the Dragonfly App.
Built-in/USB camera directly connected to the computing unit that runs the Dragonfly App.
- PRO:
- there is no need to have a reliable Wi-Fi LAN.
- minimum latency for what concerns the computation of the locations.
- more reliable because each computation unit is independent and there is not SPOF (single points of failure) for multiple assets.
Off-board local computation
 Network camera that makes available its video stream using a Wi-Fi local network to the computing unit that runs the Dragonfly App.
Network camera that makes available its video stream using a Wi-Fi local network to the computing unit that runs the Dragonfly App.
- PRO:
- the maintenance of the computing units is easier because they are NOT located on board of the assets.
- the weight on the asset is lower.
- the power consumption on the asset is lower.